Do we have to work in isolation?

Not another blog on social distancing, rather a look at the different strategies in the key international standards regarding functional insulation. The subject of the minimum insulation requirements is to ensure an integrated circuit, a mains cable, or another component does not suffer damage from flashover, i.e., a voltage breakdown within or around the device.
We have posted a couple of times in the last few months on the influence of IEC 60664 in this subject area. One key difference between IEC 60664 and the medical device safety standard IEC 60601 is the lack of functional insulation consideration in IEC 60601.
The definition of functional insulation in IEC 60664 (origins in IEC 60050):
Functional insulation
Insulation between conductive parts which is necessary only for the proper functioning of the equipment.
The other four categories to consider:
Basic insulation
Insulation of hazardous live parts that provides basic protection.
Supplementary insulation
Independent insulation applied in addition to basic insulation for fault protection.

Double insulation
Insulation comprising both basic and supplementary insulation.
Reinforced insulation
Insulation of hazardous live parts that provides a degree of protection against electric shock equivalent to double insulation.
IEC 60601 does not distinguish between basic and functional insulation, which is different from most standards such as IEC 60664 and IEC 62368. However, this is not a major issue when we are focused on safety. IEC 60664-1 states that technical committees should make a risk judgment on functional insulation and, if necessary, it shall comply with the requirements of basic insulation.

Alastair Walker, Owner & Consultant
Do you want to learn more about the implementation of IEC 60664, IEC 60601, IEC 61010, or other standards in the Automotive or Medical Device sector?
📩 Contact us at info@lorit-consultancy.com for bespoke consultancy or join one of our upcoming online courses to stay ahead in compliance and safety.
Erfahre mehrFigure 1 is an illustration of the example provided in IEC 60664-2-1 for a Class I power supply, i.e., it utilizes a protective earth. On the left of the diagram, we see that the insulation between Live and Neutral requires functional insulation. However, as mentioned above, if we are focused on a mains input with 230 V AC, then the requirement to meet basic insulation is necessary.
On the right side of Figure 1, we see the secondary output, where again functional insulation is necessary. However, in this case, as the voltage is not hazardous, the clearance requirement results in a much lower value.
The enclosure is metallic, and a protective earth is utilized, which, if meeting the requirements of, e.g., IEC 60601, has an impedance of <100mΩ and can conduct a current of 25A or 1.5 times the rated current of the device. This is an area where IEC 60601 has advantages, as the reference is always to a means of protection rather than referring to just basic or reinforced insulation. The means of protection as a protective earth supplements the basic insulation in Figure 1, hence providing a single-fault-safe system. This means only basic insulation is required between the protectively earthed enclosure and any hazardous voltage.
Table 1 summarizes the clearance requirements based on the IEC 60664 requirements and the rated impulse withstand voltage.
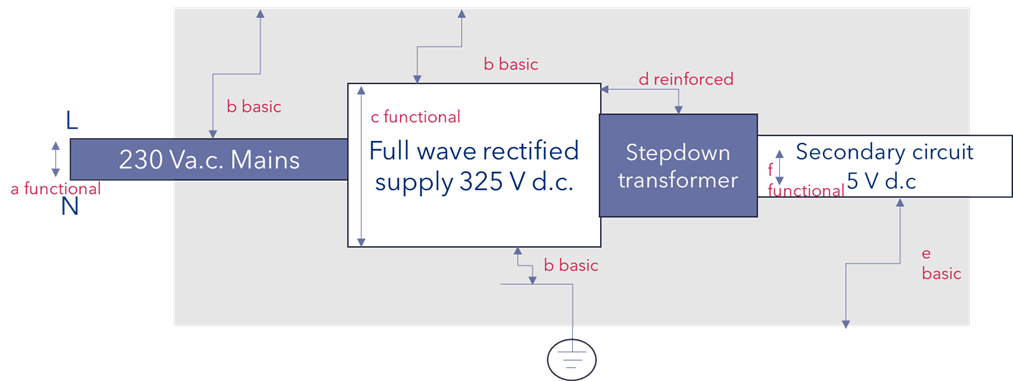
Figure 1. Insulation Diagram Class I Equipment
From IEC 60664-2-1, based on defined criteria such as the pollution degree and transient withstand voltage, we arrive at what is required for air clearance distances within the enclosure.
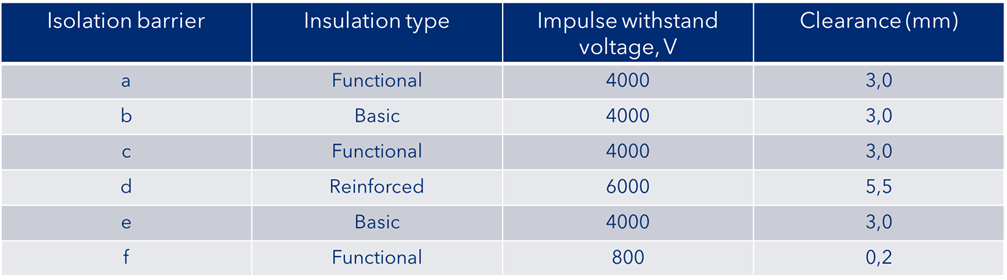
Table 1. Clearance distances for Figure 1
There are many good sources available when considering functional insulation of components, particularly integrated circuits (ICs). Texas Instruments has an excellent ‘Application Brief: Understanding Functional Isolation’, which compares the creepage and clearance distances of different IC packages. When looking at VSON packages (for functional isolators), where only functional insulation is required, a chip with 2.2mm creepage and 2.2mm clearance can be utilized, thus saving significant board space.
Table F.8 of IEC 60664-1 provides guidance on the required clearance distances based on peak, temporary, or recurring voltage (see Table 2 below).
For spaces of 2mm or less, both IEC TR 63040 and IEC 60664-5 provide good guidance on dimensioning and testing.
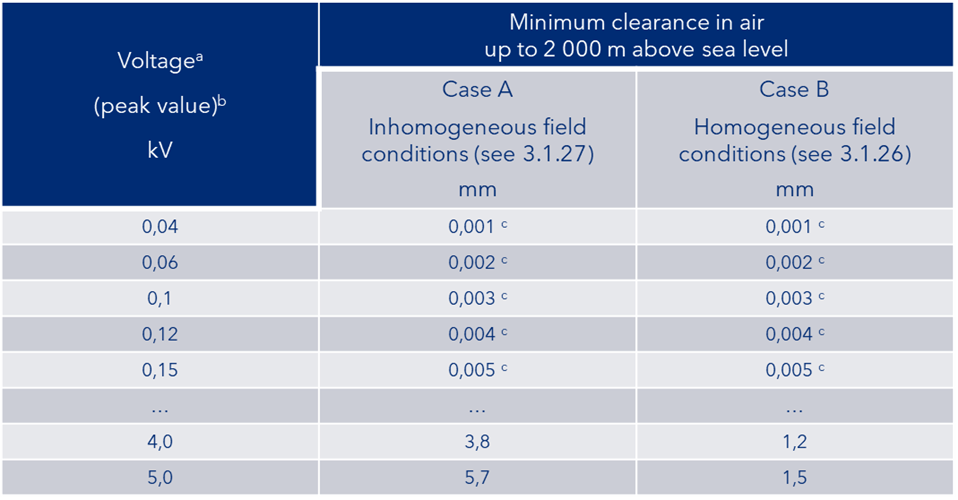
Table 2. Clearance distances from F.8 in IEC 60664-1
Insulation coordination is a tricky subject that many customers find challenging. The guidance of IEC 60664 is helpful in identifying the requirements for functional and other insulation types. Where safety is the key topic, erring on the side of caution and specifying basic insulation is the right approach. However, if the focus is on avoiding damage to external circuits, following the IEC 60664 guidance on functional insulation can reduce creepage or clearance distances significantly.
For good guidance on the application of means of protection, IEC 60601 provides reasonable coverage on this, albeit still in a cryptic form.
Edition 4 of IEC 60601 is coming!
By Alastair Walker, Owner / Consultant
Whether you need guidance on functional insulation, risk management, or regulatory compliance, we are here to help.
📩 Get in touch at info@lorit-consultancy.com or via contact form to discuss your needs or explore our expert-led training courses.